
773-123-1234
info@dreamtechcomputing.com
C#, which is pronounced C sharp, is Microsoft’s “clone” of Java. It’s a strongly-typed object-oriented language which is also platform interoperable on machines that are compatible with Microsoft’s .NET Framework. It’s usually preferred when developing software that needs to be interoperable with the different processors for Windows machines.
How Does the Language Work?
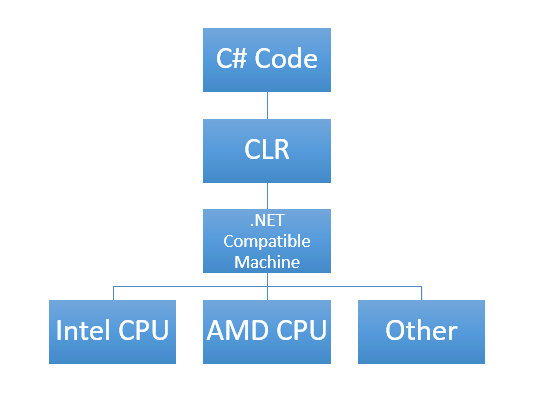
Microsoft’s .NET Framework is the required component for C# programs to run on different Windows machines. The framework provides a virtual machine called the Common Language Runtime (CLR), which acts similarly to the Java Virtual Machine. Different processors, such as Intel and AMD CPU’s, have their own ways of interpreting code, so the CLR translates the C# code into the specific machine readable code.
Benefits of C#
The benefits of using C# is primarily the interoperability on different windows machines that have Microsoft’s .NET Framework installed. C# is also a purely object-oriented language, unlike C++, which is an object/procedure-oriented language because C++ is derived from the language C. The benefit of using C# over Java when developing software on .NET compatible machines is that it’s usually more efficient and runs faster than Java.


